Any small business hoping to increase its online presence and attract more customers should invest in Search Engine Optimization (or SEO). From keyword research all the way to advanced strategies like schema markup, this ultimate guide tells you everything you need to know about SEO for small business websites. Let’s dive in!
19 minutes
Table of contents
What is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It involves optimizing your website and its pages to rank higher in search engine results, making it easier for potential customers to find your business. Effective SEO leads to increased visibility, higher web traffic, and better conversion rates, all of which are crucial for small businesses with limited marketing resources.
How do search engines work?
Search engines use bots to scan your website for new and updated content. This process is called crawling. Once a search engine’s bots crawl your website, they send the scanned content to a massive database called the Index, which houses all the data that the bots analyzed. Then, when someone searches for something via the search engine (such as Google, for example), the search engine presents content from the Index that best answers their search query. Typically, the search engine bases its results on relevance, authority, and search intent.
1. Keyword research
Keywords are the terms and phrases people type into search engines. Targeting the right keywords is necessary if you hope to create valuable content for your customers and drive traffic to your website.
How to do keyword research
- Brainstorm topics: List topics relevant to your business, products, and services. Ten to twenty keywords are a good starting point. When making your list, don’t forget to target local search queries by including locations in your keywords (for example, “sustainable furniture company Pittsburgh”).
- Use keyword tools: Try tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest to help generate ideas.
- Analyze competitors: Search for your keywords to see how your competition measures up.
- Consider search intent: Try to understand why users search for certain terms. For example, are they seeking more information, or do they want to purchase a product?
- Prioritize keywords: Focus on a mix of head terms (broad, high-volume) and long-tail keywords (specific, lower-volume).
Want a bit more guidance on conducting keyword research? Check out our guide to keyword research for small businesses!
2. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO specifically refers to strategies that optimize individual web pages on your website to improve their search engine rankings and attract relevant traffic. It involves making adjustments to both the content and the HTML source code of a page, focusing on elements that you control directly.
Title Tags
A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. It appears in two key places:
- Search engine results: The title tag is displayed as the clickable headline in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Browser tabs: It shows up at the top of the browser window or tab when someone visits your page.
Title tags help search engines understand what your page is about, which can improve your rankings and click-through rates. A well-crafted title tag will entice searchers to click through to your website to find an answer to whatever query they’ve plugged into the search engine.
Here are some tips for crafting great title tags:
- Be concise. Anything over 60 characters will be cut off in search results.
- Include your main keyword near the beginning.
- Make it descriptive and relevant to the page’s content.
- Avoid keyword stuffing; focus on clarity and natural language.
- Make each page’s title tag unique.
For a bakery’s homepage, an example title tag could be: Best Bakery in Austin, TX - Sweet Treats & Custom Cakes. Perhaps a car insurance agency might use a title tag like this: Portland's Top Locally-Owned Car Insurance Agency since 1954: Smith Insurance.
Meta descriptions
The meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a summary of a web page’s content. While it doesn’t directly influence search rankings, it plays an important role in a) helping search engines understand the context and relevance of your page’s content; and b) attracting searchers to click on your link in search engine results.
A meta description appears underneath the title tag in a search engine results page, giving searchers a snapshot of what to expect if they click through to your page.
Below are some of our tips for creating effective meta descriptions:
- Keep them under 160 characters to ensure they display properly in search results.
- Accurately summarize the content of the page. Don’t create clickbait!
- Include relevant keywords naturally, but avoid keyword stuffing.
- Make it compelling and include a call to action.
- Craft a unique meta description for every page.
Using the same bakery page example, our meta description might look like this:
<meta name="description" content="Discover the best bakery in Austin! Freshly baked bread, custom cakes, and sweet treats made daily. Order online or visit us today.">
Header tags
Header tags are HTML elements (H1, H2, H3, etc.) used to structure and organize content on a web page. They create a hierarchy that helps search engines and site visitors (especially those with disabilities) understand the main topics and subtopics of your content. There are several types of header tags:
- H1: The main heading of the page. There should typically be only one H1 per page, describing the overall topic.
- H2: Subheadings that organize the main sections under the H1.
- H3: Subsections under H2
- H4: Subsections under H3
- H5: Subsections under H4
- H6: Subsections under H5
Most of the time, you will not need to use anything beyond H3.
Here are some best practices when using header tags in your content:
- Use only one H1 tag per page, reflecting the main topic.
- Organize content logically with H2s for major sections and H3s (or lower) for subsections.
- Include relevant keywords naturally in your headings. Do not keyword stuff.
- Make headers descriptive and helpful, not just stuffed with keywords.
Content optimization
Content optimization is perhaps the biggest “chunk” of on-page SEO, as it takes up most of your effort and time. To optimize your content for search engines, you must incorporate your target keywords throughout the text. This takes some practice, because the insertion of keywords must sound natural. If you overdo it by stuffing keywords into your content too often, search engines may penalize you with lower rankings.
In addition to optimizing for keywords, you also need to improve the quality of the content itself. This means providing valuable, original, and well-organized information that matches your visitors’ search intent. Your language must be clear and concise. And don’t forget to optimize your images, too!
A general rule of thumb when optimizing, whether it is for your homepage, About page, Contact page, blog posts, or product pages, write for humans first and the search engines second. If all you do is prioritize what the search engine wants, you run the risk of missing the forest for the trees. Provide the high-quality, engaging content that your visitors want, and the search engines will reward you for that.
Internal linking
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another page on that same website. Strategically placed internal links help guide your visitors to related content and assist search engines in understanding your website’s structure.
Related: The Dos and Don’ts of Internal Linking
When placing internal links, always use descriptive anchor text that gives the search engine and site visitor an indication of what will happen when they click the hyperlink. Want some examples? Look throughout this blog post!
URL Structure
Search engines use URLs to discover and understand the content on your site. Clear, organized URLs make it easier for search engine bots to crawl your website effectively. Not only that, but short, meaningful URLs are easier to remember and look cleaner when shared on social media or other websites. They also appear more trustworthy compared to long, complex links with random characters.
Here are some tips to help create SEO-friendly URLs:
- Keep them short, simple, and descriptive
- Use keywords relevant to the page’s content
- Use hyphens to separate words, not underscores
- Avoid unnecessary parameters, numbers, or special characters.
- Always use lowercase letters
- Reflect site structure (e.g., /services/web-design)
URL structure is important for SEO because it influences how both search engines and users perceive, navigate, and understand your website. Well-structured URLs can improve your site’s visibility, click-through rates, and user experience. Below is an example of a good URL and a not-so-good URL:
Good:www.example.com/services/seo-optimization
Not so good:www.example.com/page?id=1234
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO deals with optimizing aspects of your website’s infrastructure (aka the backend “stuff”). By optimizing these things, you make it easier for search engines to crawl, index, and rank your pages more effectively. Here are some of the key components to this part of SEO.
Site speed
Fast-loading pages are essential these days. We have all been frustrated by websites that load slowly or won’t load at all. A site that loads quickly builds positive digital engagement with your business. Not to mention, there is some evidence that both load time and engagement with your content improve your rankings in the search results.
To make your web pages load efficiently, you should do the following:
- Compress your images and use web-friendly file types
- Minimize use of large scripts/plugins
- Use testing tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTMetrix to find ways to improve your site speed
- Leverage browser caching
- Minimize CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Mobile-friendliness
With 61% of all web traffic coming from mobile phones, having a great mobile-friendly website is essential as we move into 2026. Use a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes, and prioritize site speed as you optimize. Google’s mobile-friendliness test can help you with this process. It warns you about any major suboptimal features and renders a screenshot of how your site appears for the majority of mobile visitors.
Here are a few questions to keep in mind as you optimize for mobile friendliness:
- Does the width of your website automatically adjust to the screen size (“viewport”) of the visitor’s device?
- Does text automatically resize for mobile visitors, so that they don’t have to pinch-and-scroll to read it?
- Are your calls to action and other buttons large enough for people to click with their fingers and thumbs?
These kinds of adjustments are what’s known as “responsive” behavior. If your WordPress website is not yet responsive, it’s time to upgrade!
Crawlability
Search engines like Google build their database of webpages by sending robots, or “spiders” as we call them, to “crawl” websites and gather information. As a business owner, you need to make sure the spiders are crawling your website and storing its contents in the search engine’s index. The quickest way to do this is to enter [site:yourdomain.com] into Google. For example:
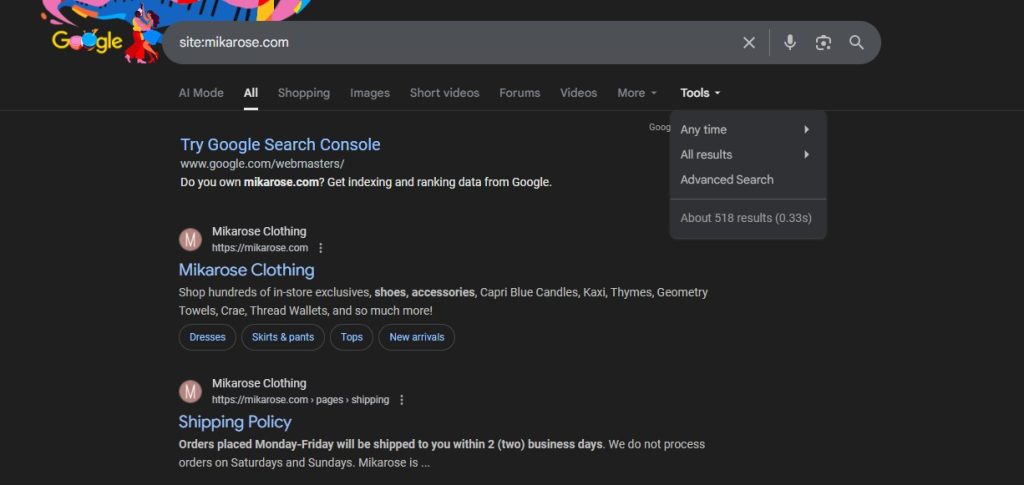
Under Tools, the farthest right option on the menu below the search bar, you can see the number of results brought up by the search. Make sure this number sounds approximately accurate. If the number sounds accurate, then the spiders are crawling and indexing your site successfully. Your job here is done!
If, however, you have a 5-page website that returns 1,000 pages or a 1,000-page site that only returns 5 results in search, you have a major technical issue with your site. Either way, register your website with Google Search Console for additional technical advice and other testing tools. At MotorClick, all our clients’ websites are connected to GSC to troubleshoot issues like this.
There may be certain pages you do not want the spiders to crawl. In this case, you need to edit your robots.txt file. Yoast wrote a phenomenal article on how to do this. But we would caution you not to edit this file unless you really know what you are doing.
Using HTTPS
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) is important from both a security and SEO standpoint. An HTTPS connection encrypts the data transmitted between a user’s browser and your website. This prevents sensitive information—like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details—from being intercepted by hackers or malicious actors. Without HTTPS, data is sent in plain text and is vulnerable to interception.
Modern browsers display a padlock icon or “secure” label for HTTPS sites, signaling to visitors that your website is safe to use. Conversely, browsers may flag HTTP sites as “Not Secure,” which can scare away potential users or customers.
Google now considers HTTPS a ranking factor and favors websites with HTTPS over those that use HTTP. This means securing your site can help improve its visibility and ranking in search engines. If you are still using HTTP, it is time to switch to HTTPS!
Fixing broken links
Broken links on your website frustrate your visitors. If they frequently encounter dead ends or 404 error pages, they are more likely to leave your site. Not only that, but a website with too many broken links looks neglected and untrustworthy to both visitors and search engines. Maintaining healthy, working links helps reinforce your site’s authority and credibility. Therefore, it is in your best interest to regularly review your website to find and fix any broken links.
Fixing broken links helps maintain a positive user experience, ensures search engines can effectively crawl and index your site, preserves the SEO value of your internal and external links, and sustains the overall authority and reputation of your website. Tools like SEMRush offer a site audit feature that will find these broken links for you and propose solutions to fix them.
Eliminating duplicate content
When multiple pages on your website have the same or very similar content, you have what we call “duplicate content”.
This can cause multiple pages to compete for the same keywords, which makes it difficult for search engines to determine which page to index and rank. The result? It doesn’t rank any of them.
If you have too much duplicate content, you might exceed what’s called the “crawl budget”. Spiders can only crawl so many pages before they need to travel back to the index. Duplicate content wastes the spider’s time and prevents it from discovering new or updated pages.
To eliminate duplicate content, follow these practical steps:
- Canonical Tags. Add a canonical tag to each page to indicate the preferred version to search engines.
- 301 Redirects. Set up permanent redirects from duplicate pages to the authoritative version.
- Consistent Linking. Always link to the preferred version of a page to reinforce which URL should rank.
- Avoid URL Variations. Use GSC’s URL Parameters tool to handle variations caused by parameters, session IDs, or tracking codes.
- Proper Pagination. If your site uses pagination (for example, in blog archives), use rel=”prev” and rel=”next” tags.
- Noindex Meta Tag. Add this tag to pages that must exist but shouldn’t be indexed (like printer-friendly versions).
- Unique Content. Make content unique on every page – no copy-pasting!
- www vs. non-www. Choose one version (e.g., https://www.example.com) and redirect all others to it.
- Check for Scraped or Syndicated Content. If your content is republished elsewhere, ask for a canonical link to your original page.
4. Local SEO
Local SEO refers to the optimization of your website for location-based queries. This means capitalizing on location-specific keywords (region, city, county, etc.), maintaining consistent NAP information across websites, directories, and platforms, and earning backlinks from local newspapers, blogs, business associations, and community sites to strengthen your local authority.
Perhaps most importantly, you need to claim and optimize your Google Business Profile. This profile allows your business to appear in Google Maps and local search results. It also allows customers to leave ratings and reviews for your business – be sure to respond to these to further boost engagement and trustworthiness!
5. Content Marketing
Content marketing is a strategic approach to creating, publishing, and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a clearly defined audience — with the ultimate goal of driving profitable customer action.
Key Elements of Content Marketing
1. Valuable Content:
Instead of directly pitching products or services, content marketing focuses on providing information, insights, entertainment, or solutions that genuinely benefit the target audience.
2. Audience-Centric:
Content is tailored to the needs, interests, and pain points of a specific audience, making it more effective in building trust and long-term relationships.
3. Variety of Formats:
Content marketing can take many forms, including blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, social media updates, eBooks, webinars, and newsletters.
4. Consistency:
Regular production and distribution of content help maintain audience engagement and reinforce the brand’s authority in its niche.
5. Distribution and Promotion:
Successful content marketing doesn’t stop at creation — content must be shared through appropriate channels (such as social media, email, or partnerships) to reach your audience.
Benefits of Content Marketing
- Builds Trust and Authority: By consistently delivering valuable content, businesses establish themselves as experts in their field.
- Improves SEO: High-quality content increases website visibility, attracts backlinks, and boosts search engine rankings.
- Engages and Educates Audiences: Content helps inform potential customers, answer their questions, and guide them through the buyer’s journey.
- Generates Leads: Effective content can prompt users to take action, such as subscribing to a newsletter or filling out a contact form.
- Supports Other Marketing Channels: Content can be repurposed across various platforms, amplifying its impact.
Content marketing is about earning attention and trust by delivering genuinely useful or entertaining material. It’s a long-term strategy that helps brands build relationships, drive traffic, and ultimately convert prospects into loyal customers.
6. Off-page SEO
In contrast to on-page SEO, off-page SEO refers to all the strategies you use outside your own website to improve its authority and rankings in search. In other words, things like link building, social media, and reviews on third-party sites. Off-page SEO is all about building your website’s reputation, authority, and visibility beyond its own pages.
Link building
Link building is the most prominent aspect of off-page SEO, and often the hardest to accomplish. It involves acquiring high-quality backlinks (links from other websites TO your website). These signal to search engines that your site is trustworthy and authoritative. You can build backlinks in the following ways:
- Submitting guest blogs to reputable blogs in your industry
- Listing your website on relevant resource pages and in industry directories
- Collaborating with industry leaders or influencers
- Getting your website mentioned in online publications, forums, and communities
Marketing on social media
When you share your website’s content on social media platforms, you increase digital reach, encourage engagement with your customers, build brand awareness, and drive traffic back to your website.
Related: 7 Ways to Level Up Your Social Media Strategy
Reviews and local listings
Encouraging positive reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, and industry-specific directories improves your business’s reputation and local search rankings.
Read More: How and Where to Get Reviews for Your Business
7. Monitoring analytics to improve SEO
If you want to not only claim the top spot in the search results but also continue to stay there, SEO is not something you can ever really check off your to-do list. By monitoring your website traffic, audience data, and search result performance, you can continue making improvements to your site over time.
Here are two analytics tools every small business owner needs to connect to their website:
- Google Analytics: track website traffic, user behavior, bounce rate, and conversions.
- Google Search Console: monitor search performance, keyword rankings, crawl errors, and index status
Conduct regular SEO audits to identify and fix any issues. So long as you continue to make improvements, you will see the fruits of your labors with time!
8. Advanced SEO strategies
In this section, we will briefly cover some of the more advanced SEO strategies out there for small business owners ready to take the next step with the SEO of their website.
Voice search optimization
Use of voice-activated assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri continues to rise. As more and more people use their smartphones and smart speakers to search instead of typing, optimizing for voice search is becoming an important SEO strategy.
Here are some tips to help you start optimizing your website for voice search:
- Add relevant schema markup to your site (more about this below)
- Integrate natural, question-based phrases and long-tail keywords into your content
- Provide concise, well-structured answers to commonly asked questions
- Use lists and tables whenever possible to simplify your content
- Ensure your Google My Business listing is accurate
- Use local keywords in your website content
- Optimize your page loading speed (see above for more information)
- Add an FAQ page that addresses common queries related to your business and industry
Voice search optimization involves making your content more conversational, direct, and locally focused, while ensuring your site is technically sound. By doing so, you’ll better serve users who search with their voices—and position your website for greater visibility as voice search continues to grow.
Schema markup
Schema markup is a type of structured data code that you add to your website’s HTML to help search engines better understand the content on your pages. It uses a vocabulary called Schema.org to define and label different elements of your website—such as articles, products, reviews, events, and more.
When you add schema markup, you’re providing extra context so search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo can interpret your content more accurately. This can enhance your search listings with “rich results” (also known as rich snippets), such as star ratings, event details, FAQs, recipe instructions, and other visually distinctive elements that appear in search results.
A couple of key points to remember:
- Schema markup is not visible to regular visitors; it’s for search engines.
- It improves SEO by making your pages more eligible for enhanced displays in search results.
- It can be added in various formats, such as JSON-LD (preferred), Microdata, or RDFa.
Video SEO
Video SEO is exactly what it sounds like: optimizing your video content to help it rank higher in the search results and on platforms like YouTube and Rumble. The goal is to increase the visibility of your videos, attract more viewers, and drive more engagement or traffic.
Most aspects of video SEO are similar to those of written content on your site, like doing keyword research, creating compelling titles and descriptions, improving site speed, and optimizing for mobile. There are some other aspects, however, that are specific to video:
- Transcripts and Captions: Providing transcripts or closed captions makes your videos accessible and gives search engines text to crawl and index.
- Video Schema Markup: Adding structured data to pages that contain a video helps search engines understand the video and can enable rich snippets (like video thumbnails) in search results.
- Thumbnail Optimization: Using custom, engaging thumbnails to increase click-through rates.
- Video Sitemaps: Submitting a video sitemap to search engines helps them find and index your video content more efficiently.
- Engagement Metrics: Encouraging likes, shares, comments, and watch time, as these factors can influence rankings, especially on platforms like YouTube.
Optimized videos are more likely to appear in Google’s video results, YouTube search, and as rich snippets. Moreover, effective video SEO increases the chances of your content being discovered by a larger audience.
International SEO
International SEO involves making adjustments to help your website rank well in search results in different countries. If your website sells products to countries outside the United States, or if you have a blog that you want others outside your country of origin to be able to access, international SEO is worth investigating.
Note: international SEO is for very advanced SEOs and website developers/designers. Do not try this on your own if you do not know exactly what you are doing. Mistakes with international SEO can have detrimental effects on your website’s performance in search results.
Here are some of the key aspects of international SEO to consider:
- Geo-Targeting: Configuring your website (through settings in Google Search Console, hreflang tags, or country-specific domains) so search engines know which countries your content is intended for.
- Hreflang Tags: Adding hreflang annotations to your website’s code to indicate the language and regional targeting of each page. This helps search engines serve the correct language or regional version to users based on their location and language preferences.
- Localized Content: Creating and optimizing content in the native languages of your target audiences. This includes proper translation and cultural adaptation, rather than just direct translation.
- Country-Specific Domains or Subdomains: Using country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) like .fr for France or .de for Germany, or creating subdomains/subdirectories (e.g., fr.example.com or example.com/fr/) for different regions.
- Local Backlinks: Building links from authoritative local websites to boost your site’s authority in specific countries.
- Technical SEO: Ensuring that your site structure, URL formats, and metadata are optimized for international targeting.
- Local Search Engines: Considering optimization for country- or region-specific search engines (like Baidu in China or Yandex in Russia), not just Google.
International SEO can help your website reach a global audience more effectively, as it ensures that users living in different countries can find a version of your site in their language. This can, therefore, increase search traffic, brand awareness, and conversion in international markets.
Conclusion
SEO is an ongoing process that requires dedication, research, and adaptation to evolving search engine algorithms. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you’ll build a strong foundation for your website’s long-term success. Remember, the ultimate goal is to create value for users and provide them with the best possible online experience.
Ready to start optimizing? Implement these tips and watch your website rise through the search rankings! It’s only a matter of time!
Keep Reading: Find Out Which Pages of Your Website Rank High on Google

